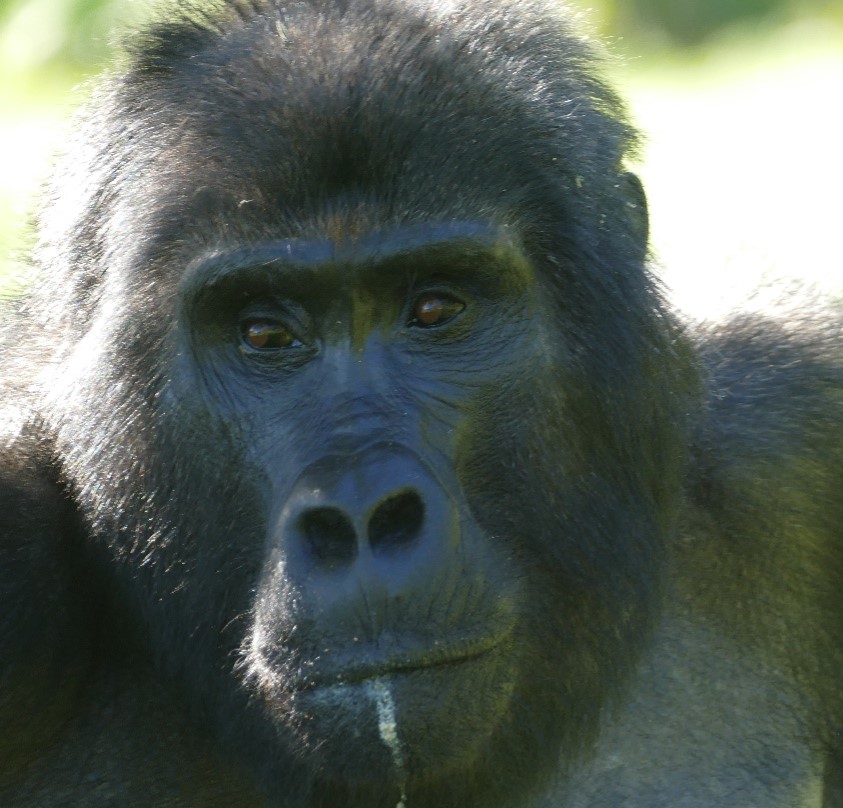
BIKYINGI
12 Members: Last updated 31/01/2024
Bikyingi group is found in Rushaga tourism sector of Bwindi Impenetrable National Park. The group is currently led by Silverback Kaharata who assumed leadership after killing the then dominant Silverback Bikyingi from whom the group name was derived. Bikyingi died after a fight with the then solitary male in Bikyingi area. The duo had had a series of fights before and this was the climax of them. Rangers suspect that the solitary male had interest in the leadership of the group. After the death of the dominant Silverback Bikyingi all the group members dispersed and some joined other groups, for instance, about 7 individuals joined Kahungye group. However, a close search was done and 9 members including the solitary male were found. The group is currently composed of 9 individuals including, 1 Silverbacks, 2 Adult females, 3 Blackbacks, 2 Sub-adult females and 1 Sub-adult male.